Starward
An open source Python library for transparent astronomical calculations that show their work.
The Problem
Most astronomy libraries treat calculations as black boxes. You feed in coordinates, get back a result, and hope it's correct. When something looks wrong, you're stuck debugging without visibility into the intermediate steps.
I wanted a library where I could see exactly what was happening at each stage—every coordinate transformation, every time conversion, every position calculation. Not just for debugging, but for understanding.
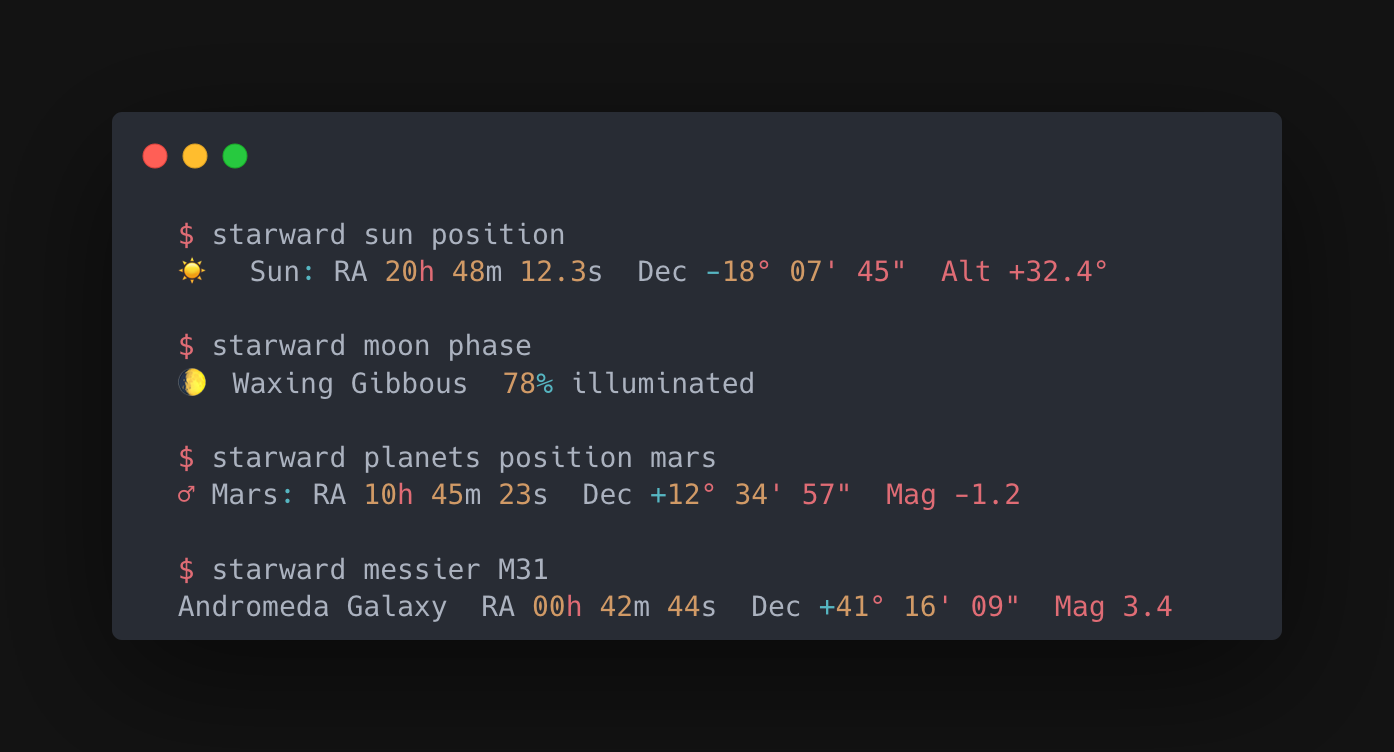
What Starward Does
Starward is a Python library and CLI tool for astronomical calculations. It computes positions, times, and coordinates while optionally showing every mathematical step.
from starward import Observer, Sun
observer = Observer(latitude=64.1, longitude=-21.9)
sun = Sun(observer)
print(sun.rise())
print(sun.set())
print(sun.altitude())
- Time Calculations - Julian dates, Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time, Local Sidereal Time
- Solar & Lunar - Positions, rise/set times, phases, twilight
- Planetary Positions - Mercury through Neptune with magnitudes
- Coordinate Transforms - ICRS, Galactic, and Horizontal systems
- Observation Planning - Airmass, visibility, transit predictions
- Object Catalogs - Messier, NGC, IC, Caldwell, Hipparcos
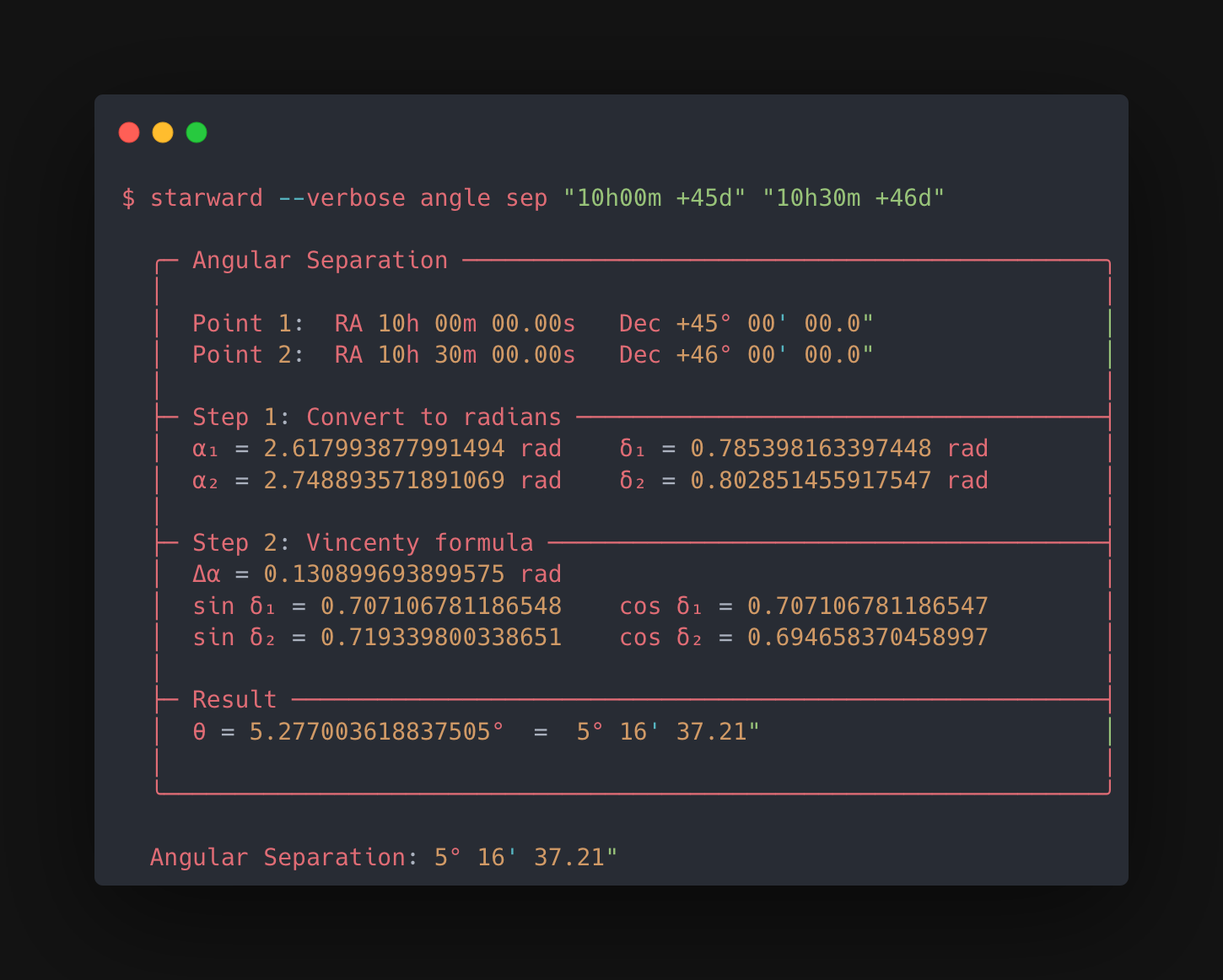
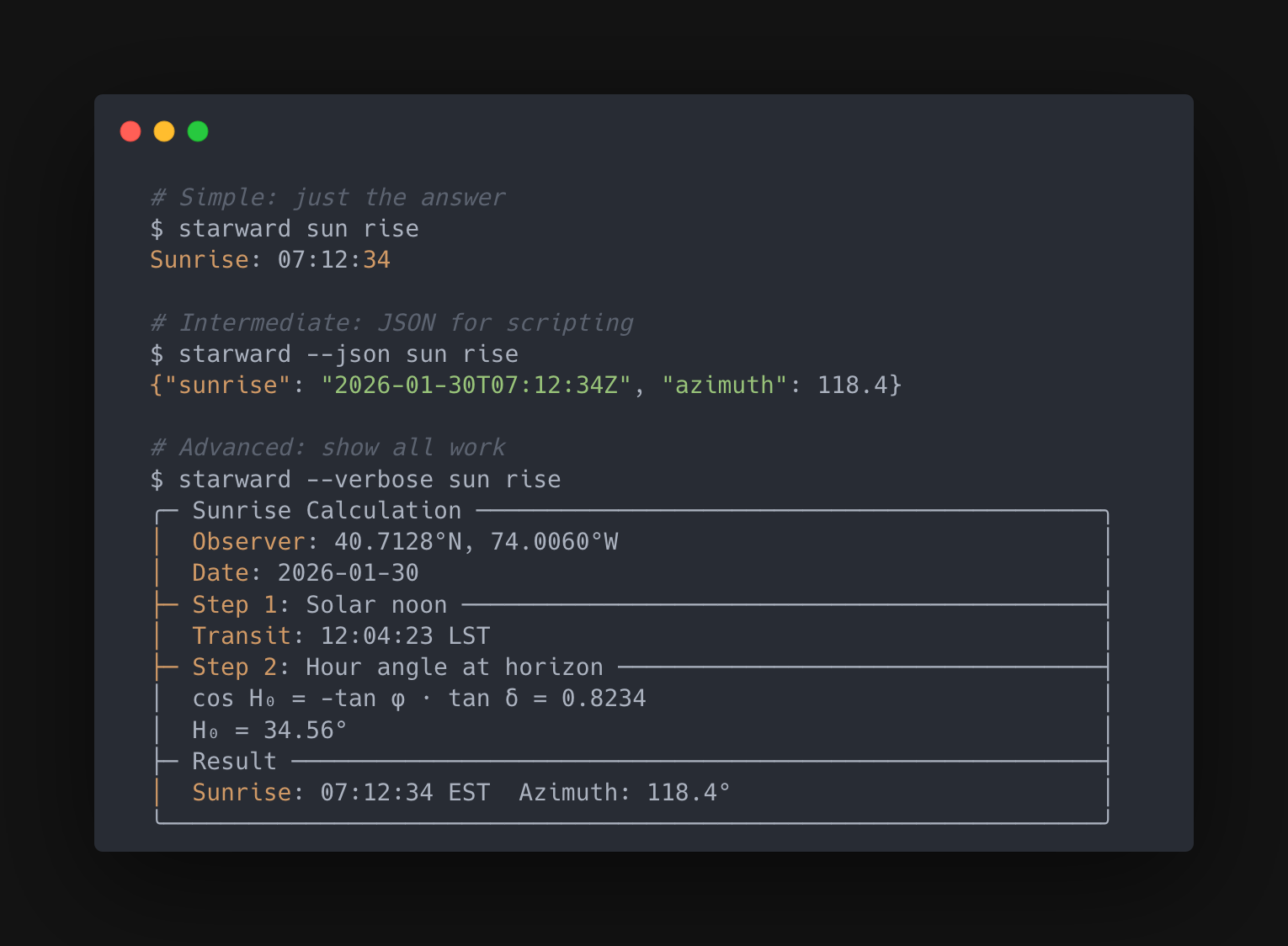
Verbose Mode
The core feature. Enable it and Starward logs every logical step:
starward sun --location 64.1,-21.9 --verbose
Computing solar position for 2024-12-21 12:00 UTC...
Julian Date: 2460664.0
Centuries since J2000: 0.2497
Mean longitude: 359.876°
Mean anomaly: 356.291°
Equation of center: -0.082°
True longitude: 359.794°
Obliquity of ecliptic: 23.437°
Right Ascension: 17h 58m 12s
Declination: -23° 26' 14"
Converting to horizontal coordinates...
Altitude: -2° 14' 33"
Azimuth: 182° 05' 41"
When a result looks wrong, you can trace exactly where the math diverged from expectation.
Building It
Published early, let feedback shape direction. The astronomy community pointed out which features mattered and which I was overcomplicating.
Coordinate transformations went through three rewrites. Converting between ICRS, Galactic, and Horizontal systems while handling precession and nutation is hard. Verbose mode helped me debug my own library.
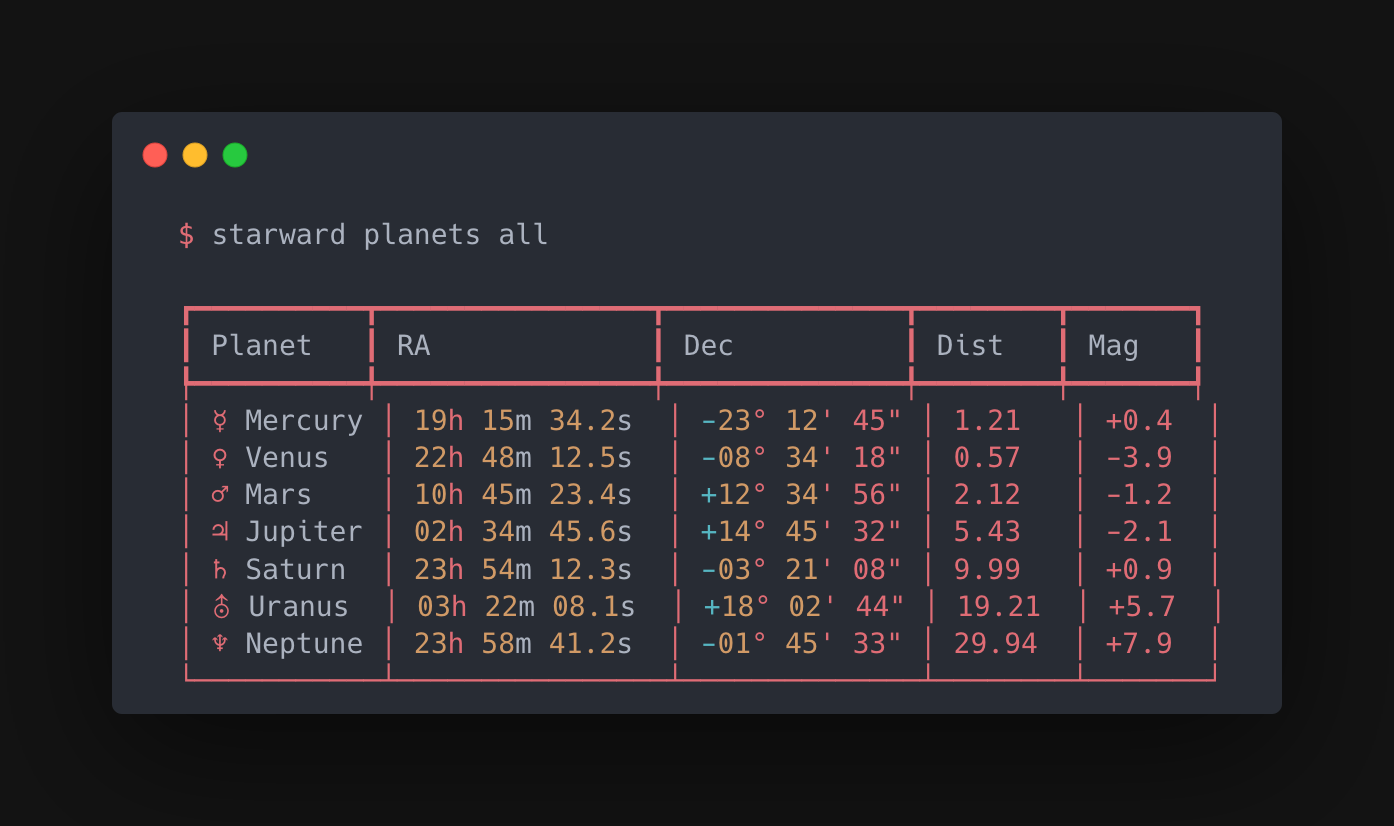
The test suite has 500+ tests validated against authoritative sources—USNO, JPL, IAU. Pure Python with no compiled dependencies, so it runs anywhere.
Documentation
The docs at starward.dev mirror the library's philosophy: show the work. Each function includes not just usage examples but the mathematical formulas behind them.
Lessons
Ship before you're ready. Early feedback beats polish.
Write docs as you build. I thought I'd add them later and forgot my own design decisions.
Visibility beats cleverness. The verbose logging I built for users turned out to be essential for development.
What's Next
More catalog coverage and better observation planning tools. The goal stays the same: make astronomical calculations transparent and educational.